Jan . 20, 2025 05:11
Back to list
what is the lockstitch sewing machine
The lockstitch sewing machine stands as a cornerstone of modern textile production, offering a blend of durability and precision that has propelled the craft of sewing into an era of advanced craftsmanship. Recognized as the most common mechanical stitch generated by both domestic and industrial sewing machines, the lockstitch is the quintessential stitch that underlines clothing construction, upholsteries, and a myriad of fabric applications.
Regarding authoritativeness, the lockstitch sewing machine has a storied legacy. Patented by Elias Howe and perfected by Isaac Singer in the 19th century, it revolutionized the sewing industry. Today, leading brands like Singer, Brother, and Juki continue to refine this technology, infusing innovations that cater to both traditional and contemporary sewing needs. The trustworthiness of the lockstitch sewing machine can be observed in its widespread adoption across diverse industries. Educational institutions use these machines to train future designers, while manufacturing environments employ them for large-scale productions. Their widespread use is a testament to their reliability and effectiveness. In crafting an SEO-friendly article around lockstitch sewing machines, one must not overlook the importance of addressing user intent and providing valuable insights. Potential buyers often seek information on durability, specific models, and maintenance tips. Including direct comparisons of popular models, discussing pros and cons, and offering practical maintenance advice can boost engagement. Concluding, the lockstitch sewing machine embodies a blend of historical significance and modern-day practicality. Whether one is an enthusiastic hobbyist or an experienced professional, understanding and utilizing the lockstitch sewing machine remains integral to achieving excellence in sewing. As technology advances, so too does the scope and precision of lockstitch capabilities, promising a future where quality and efficiency in textile production are continually enhanced.
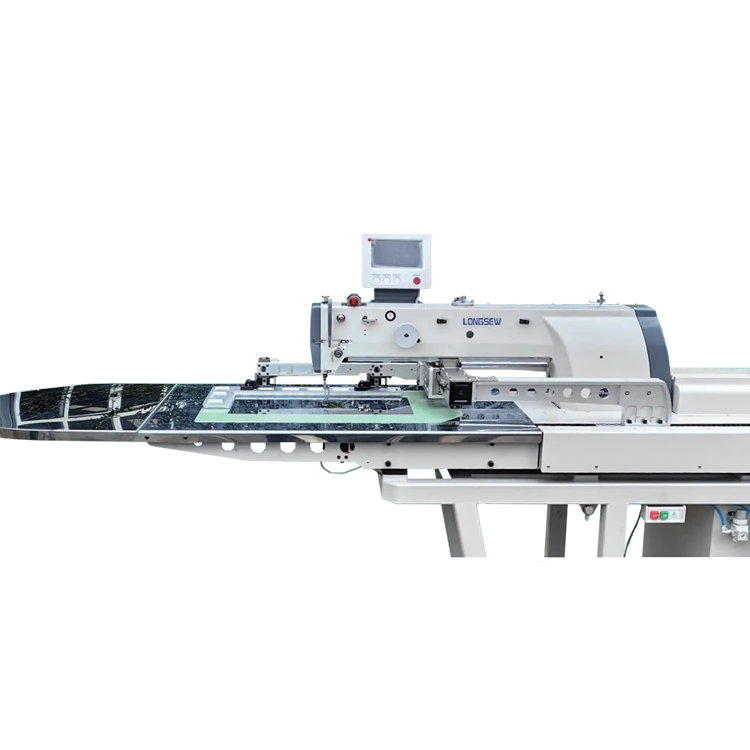
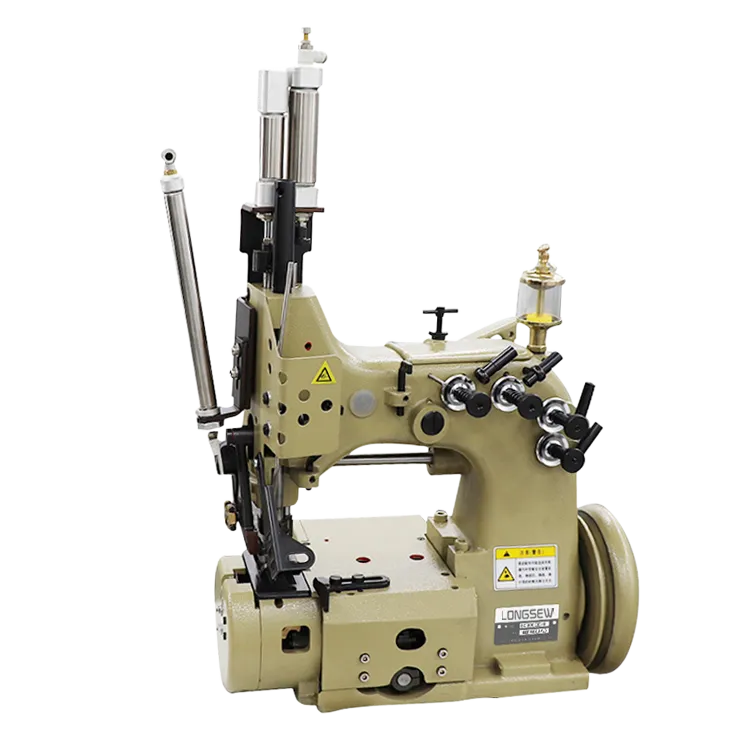

Regarding authoritativeness, the lockstitch sewing machine has a storied legacy. Patented by Elias Howe and perfected by Isaac Singer in the 19th century, it revolutionized the sewing industry. Today, leading brands like Singer, Brother, and Juki continue to refine this technology, infusing innovations that cater to both traditional and contemporary sewing needs. The trustworthiness of the lockstitch sewing machine can be observed in its widespread adoption across diverse industries. Educational institutions use these machines to train future designers, while manufacturing environments employ them for large-scale productions. Their widespread use is a testament to their reliability and effectiveness. In crafting an SEO-friendly article around lockstitch sewing machines, one must not overlook the importance of addressing user intent and providing valuable insights. Potential buyers often seek information on durability, specific models, and maintenance tips. Including direct comparisons of popular models, discussing pros and cons, and offering practical maintenance advice can boost engagement. Concluding, the lockstitch sewing machine embodies a blend of historical significance and modern-day practicality. Whether one is an enthusiastic hobbyist or an experienced professional, understanding and utilizing the lockstitch sewing machine remains integral to achieving excellence in sewing. As technology advances, so too does the scope and precision of lockstitch capabilities, promising a future where quality and efficiency in textile production are continually enhanced.
Previous:
Latest news
-
Boost Production Efficiency with a Pattern Sewing MachineNewsAug.29,2025
-
Industrial Excellence with the Best Heavy Duty Sewing MachineNewsAug.29,2025
-
Precision and Power with the Best Pattern Sewing MachineNewsAug.29,2025
-
Reliable Bulk Packaging Starts With the Right FIBC Sewing MachineNewsAug.29,2025
-
Advanced Packaging Solutions: Elevate Productivity with Jumbo Bag Sewing Machine and Industrial Stitching EquipmentNewsAug.29,2025
-
High-Performance Solutions for Bulk Packaging: FIBC Sewing Machine and MoreNewsAug.29,2025
-
Maximize Efficiency with an Industrial Cylinder Arm Sewing MachineNewsAug.28,2025


























