Advanced Techniques for Operating a Cylindrical Sewing Machine Efficiently and Effectively
The Evolution and Importance of the Cylindrical Sewing Machine
Sewing machines have come a long way since their inception in the early 19th century. Among the various designs that have emerged, the cylindrical sewing machine stands out for its unique application and design features. Unlike standard flatbed sewing machines, cylindrical sewing machines are specifically engineered to accommodate tubular fabrics and garments, making them indispensable in the garment manufacturing industry.
Design and Functionality
The cylindrical sewing machine is characterized by its cylindrical arm, which allows for sewing around curved surfaces and in tight spaces that would be challenging for a traditional flatbed machine. This design is particularly advantageous for sewing items like sleeves, cuffs, and the legs of trousers. The machine's ability to navigate around these curves and corners without distortion of the fabric is key to creating high-quality garments.
Additionally, cylindrical sewing machines often come equipped with specialized features such as adjustable stitch length, automatic threading mechanisms, and interlocking needle systems. These added functionalities not only enhance precision but also improve the sewing process's efficiency, allowing for faster production times without compromising quality.
Applications in the Garment Industry
The primary application of cylindrical sewing machines is in the mass production of apparel. They are widely used in the production of sportswear, swimwear, and knit garments, where elasticity and fit are crucial. The capability to handle various types of fabrics—from heavy denim to delicate jersey knit—makes these machines versatile tools in any sewing workshop.
Moreover, cylindrical sewing machines have also found applications in other industries beyond garment manufacturing. For instance, they are utilized in the production of bags, shoes, and upholstery where curved seams are a common requirement. This adaptability underscores their importance across different sectors, making them a valuable asset for manufacturers.
cylindrical sewing machine
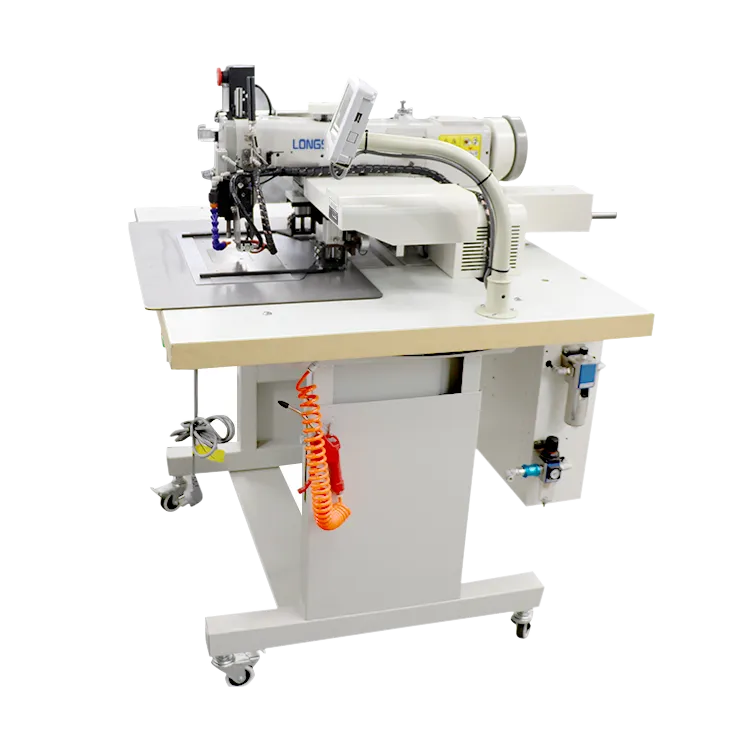
Advancements in Technology
With the continuous advancements in technology, cylindrical sewing machines have evolved significantly. Modern versions now feature computerized systems that allow for intricate designs and patterns to be sewn with ease. Digital interfaces enable operators to customize settings for different materials and stitch types, promoting efficiency and consistency.
Moreover, the integration of automation in cylindrical sewing machines has revolutionized the manufacturing process. Automated feed systems and robotic arms can perform repetitive tasks with high precision, significantly reducing labor costs and production time. This shift towards automation enables factories to scale up operations while maintaining the flexibility to produce customized garments.
Training and Skill Development
Despite the technological advancements, operating cylindrical sewing machines requires a certain level of skill and training. Operators need to understand the machine's mechanics, fabric properties, and the types of stitching techniques suitable for various applications. Therefore, training programs focused on developing these skills are essential to ensure that workers can fully leverage the capabilities of these machines.
Educational institutions and vocational training centers are increasingly incorporating courses on advanced sewing technology into their curriculums, preparing a new wave of skilled labor for the industry. This emphasis on skill development is critical for maintaining high production standards and fostering innovation in garment manufacturing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cylindrical sewing machines play a vital role in the modern garment industry. Their unique design and adaptability to various applications have made them essential for producing high-quality garments efficiently. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of cylindrical sewing machines are expected to expand even further, underscoring their importance in not only fashion manufacturing but also in diverse industries requiring precision sewing. The future looks bright for this ingenious piece of machinery, as it remains a cornerstone of textile manufacturing.
-
Heavy Duty Leather Sewing Machine: A Must-Have for Professional LeatherworkNewsMay.28,2025
-
Leather Sewing Machine: Essential for High-Quality LeathercraftNewsMay.28,2025
-
Extra Heavy Duty Sewing Machine for Premium Leather ApplicationsNewsMay.28,2025
-
Walking Foot Cylinder Arm Sewing Machine: Precision and Power CombinedNewsMay.28,2025
-
Industrial Cylinder Arm Sewing Machine: Engineered for High-Performance StitchingNewsMay.28,2025
-
Cylinder Bed Sewing Machine: A Powerful Solution for Precision StitchingNewsMay.28,2025
-
Zigzag Sewing MachineNewsMay.12,2025





























