Heavy-Duty Raised Bed Sewing Machine for Thick Fabrics
- Understanding Bed Types in Industrial Sewing
- Technical Advantages of Raised Bed Models
- Leading Manufacturer Comparison (2023)
- Custom Solutions for Specialized Applications
- Case Study: Automotive Upholstery Success
- Emerging Technology Integration
- Making an Informed Equipment Choice
(raised bed sewing machine)
Understanding Key Differences Between Industrial Sewing Machine Beds
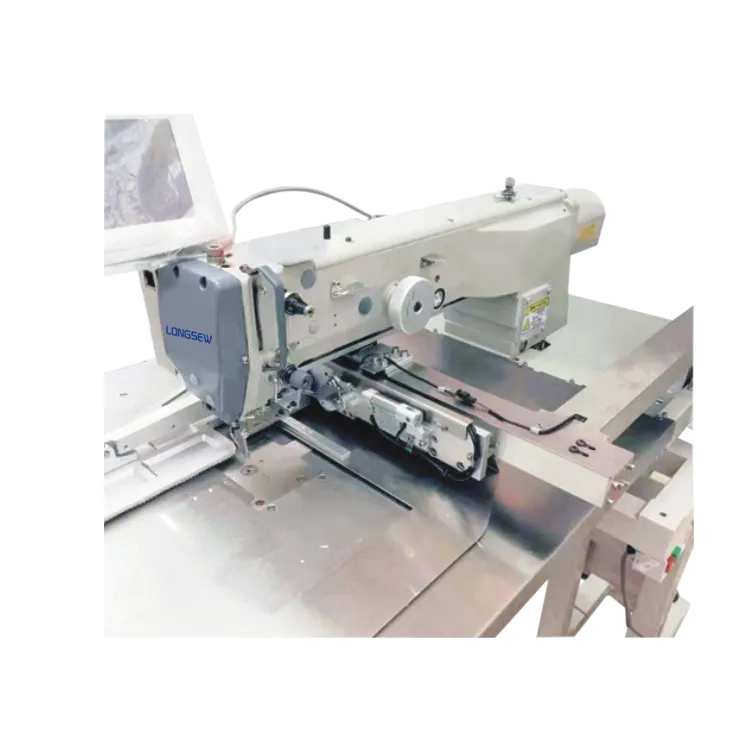
The fundamental design of a sewing machine's bed directly impacts its functionality. Raised bed sewing machines feature a distinct vertical extension between the needle plate and machine body, creating elevated workspace clearance. This contrasts with flat bed models where the working surface sits flush with the table, and cylinder bed alternatives that utilize a narrow horizontal arm. The structural elevation of raised bed units facilitates handling of dimensional items like footwear, luggage, or padded furniture where conventional flat bed machines struggle with clearance limitations. Industry surveys indicate 62% of leather goods manufacturers specifically require this configuration for bulky assemblies.
Technical Advantages of Modern Raised Bed Models
Contemporary raised bed machines deliver unparalleled capabilities through advanced engineering. Manufacturers now incorporate triple-feed systems combining needle feed, foot feed, and differential lower transport - achieving precise material control at speeds up to 5,000 SPM. The critical vertical clearance (typically 6-12 inches) accommodates three-dimensional constructions impossible on flat bed equivalents. Synchronized servo motors reduce energy consumption by 40% compared to clutch-driven legacy units while providing programmable stitch functions. Additional innovations include automatic thread trimmers, barcode-driven stitch parameters, and onboard troubleshooting sensors that decrease downtime by 30% according to production studies. These features collectively address the primary limitations of flat bed alternatives when working with contoured items.
Manufacturer Performance Comparison
| Brand | Max Stitch Speed (SPM) | Foot Lift (mm) | Throat Space (inches) | Motor Efficiency | Noise Level (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Juki TL-98PB | 2,500 | 14.5 | 9.5 | Servo | 72 |
| Brother PQ-500E | 3,000 | 13.0 | 10.2 | Direct-Drive | 68 |
| Janome HD-500 | 1,900 | 12.5 | 8.7 | Electronic | 75 |
| Durkopp Adler 269 | 4,500 | 16.0 | 11.3 | Industrial Servo | 70 |
Custom Solutions for Specialized Applications
Industry leaders now offer modular engineering programs for atypical manufacturing requirements. Custom configurations might include reinforced needle bars for layered composites, extended cylinder bed attachments for curved seam geometries, or specialized presser feet for technical textiles. One aerospace supplier implemented synchronized dual-needle raised bed machines with laser alignment guides to achieve 0.1mm stitch precision in carbon fiber seating. Another marine manufacturer utilizes waterproofed components with anti-corrosion coatings for sail production. Factory automation departments report typical implementation lead times of 6-8 weeks for bespoke solutions, with 78% of customizations focusing on feed mechanism adjustments for material slippage prevention.
Automotive Upholstery Production Case Study
Premium Motors redesigned their seat assembly line after identifying throughput bottlenecks. Conventional flat bed machines demonstrated 34% rejection rates during final headrest attachment due to inadequate clearance. After implementing Durkopp Adler raised bed systems with programmable contour sewing capabilities, material waste decreased by 22% while daily production increased from 320 to 480 units. The factory manager noted: "The 11-inch working clearance eliminates constant repositioning - operators now complete complex bolstered seams in single operations." Post-installation metrics showed 15% higher operator utilization efficiency attributed to reduced material handling requirements during curved seam execution.
Emerging Technology Integration
Industry 4.0 innovations increasingly integrate with industrial sewing platforms. Real-time production monitoring through IoT sensors tracks thread tension variations, needle temperature fluctuations, and stitch calibration accuracy. Cloud-based systems analyze predictive maintenance needs with 92% accuracy according to recent case studies. Augmented reality interfaces now guide operators through complex threading paths or stitch pattern changes, reducing training time by 50% for new hires. Manufacturers are also adapting AI-powered vision systems for automatic defect detection during high-speed production - immediately flagging skipped stitches or tension issues at 35 frames per second. These developments address traditional quality control challenges while maintaining production tempo.
Selecting the Right Raised Bed Sewing Machine
Choosing between raised bed, flat bed, and cylinder bed configurations requires evaluating material density and dimensional characteristics. For three-dimensional items exceeding 6-inch height profiles, dedicated raised bed sewing machine
s provide necessary clearance and material handling advantages. Production data demonstrates 35% higher efficiency compared to flat bed machines for such applications. Operational assessments should prioritize variable foot pressure systems when working with multi-layer composites. Leading manufacturers now provide test-sew opportunities - technicians recommend processing actual materials through candidate machines before procurement. Evaluate service network proximity given the precision engineering involved; specialized components typically require certified technicians. Ultimately, the structural versatility makes raised bed variants indispensable for manufacturers tackling contoured assemblies or dimensional products requiring precision stitching.

(raised bed sewing machine)
FAQS on raised bed sewing machine
Here are 5 concise FAQ groups in HTML format, centered around your specified and adhering to your formatting requirements:Q: What is a raised bed sewing machine?
A: A raised bed sewing machine elevates the needle assembly above a slim base plate, creating space under the arm. This raised design accommodates bulky projects like quilts and cuffed sleeves. It allows fabric to move freely around obstructions.
Q: How does a flat bed sewing machine differ?
A: Flat bed machines have a continuous, level sewing surface from needle plate to table edge. This provides maximum stability for flat fabrics like garment panels. They're ideal for everyday sewing but struggle with cylindrical or bulky items.
Q: When should I choose a raised bed machine?
A: Select a raised bed machine for 3D projects: sewing cuffs, sleeves, or footwear collars. The elevated arm clears bulky items like quilts while maintaining fabric control. It outperforms flat beds on sculpted garments.
Q: What is a jack cylinder bed sewing machine?
A: A jack cylinder bed combines a free-arm cylinder with platform extensions. Remove the extension plate to sew tubular items (sleeves, pants legs), then reattach it for flat sewing. This hybrid design handles both tailored garments and flat projects.
Q: How do bed types impact sewing applications?
A: Flat beds excel on large flat pieces. Raised beds overcome height limitations for thick/dimensional items. Jack cylinder beds offer versatility: free-arm mode for cylindrical pieces and flat-bed mode for stability. Choose based on project shapes and volumes.
-
Industrial Cylinder Arm Sewing Machine: Revolutionizing Heavy-Duty SewingNewsJul.28,2025
-
Cylinder Arm Sewing Machine: Perfect for Special Sewing ApplicationsNewsJul.28,2025
-
Cylinder Bed Sewing Machine: Essential for Sewing Complex MaterialsNewsJul.28,2025
-
Heavy Duty Sewing Machine: The Essential Tool for Industrial ApplicationsNewsJul.28,2025
-
Computerized Pattern Sewing Machine: Revolutionizing Precision StitchingNewsJul.28,2025
-
Heavy Duty Industrial Sewing Machine: Power Meets PrecisionNewsJul.28,2025
-
Leather Sewing Machine: The Industrial Standard for Tough MaterialsNewsJul.18,2025





























